In this article, we are going to study about series and parallel circuits (with some calculations). We will take a simple circuit example to learn better about series and parallel circuit with practical example. But, before discussing the series and parallel circuit, we should know about the circuit, what is a circuit? or what is an electrical electronics circuit? So, let me write the simplest definition of an electrical circuit.
An electrical circuit is a path in which "ELECTRONS" from a voltage or current source flow.
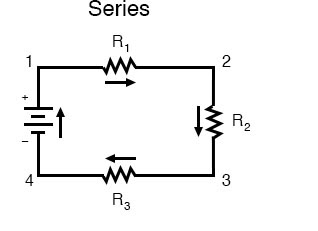
Series Circuit
A Series circuit is a type of circuit in which we have only one route of current to flow.
For example, we have two bulbs or resistors connected in a circuit with a battery, and the positive terminal of the battery is connected with first terminal of 1st resistor, second terminal of 1st resistor is connected with first terminal of second resistor, and second terminal of second resistor is connected with negative terminal of the battery. That is a series circuit.
Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, the electrical flow may stream along different ways prior to getting back to the force source.
The Voltage in a parallel circuit is something similar across the entirety of the heaps in the circuit. In a parallel circuit, the amperage is split across the entirety of the heaps. In the event that one of the heaps in a parallel circuit quits working, different burdens in parallel will actually want to keep on working. "Potential distinction is something very similar across all the part. In more straightforward terms indistinguishable bulbs associated in parallel will all be at a similar brilliance."
This is the simplest explanation of series and parallel circuit. Hope this will understand this concept. You may write below in the comment section if there is anything you have any problem in series parallel circuit concepts.




Dear visitor. Click on "Follow" button from right side above and sign in with your Gmail account. Write unlimited comments on every post. 100% Free